Why Gablofen® for Your Patients
What Gablofen Does
Gablofen is for patients who do not have relief, or have side effects they cannot tolerate from taking baclofen orally.2
If oral baclofen did not relieve your patient’s spasticity or caused side effects that he or she could not tolerate, Gablofen may be an option, starting with an intrathecal baclofen screening trial.
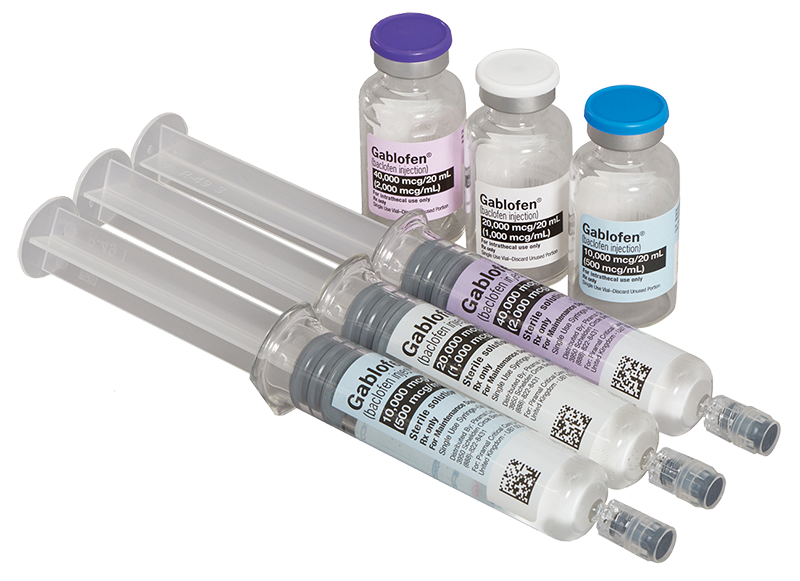
GABLOFEN IS THE ONLY FDA-APPROVED INTRATHECAL BACLOFEN IN PREFILLED SYRINGES AND FACTORY-SEALED VIALS.1,2
GABLOFEN IS INDICATED FOR PATIENTS AGED 4 YEARS AND OLDER WITH SEVERE SPASTICITY CAUSED BY DAMAGE TO THE CEREBRAL OR SPINAL ORIGIN.2
BY DELIVERING BACLOFEN DIRECTLY TO THE SPINAL FLUID, A MUCH MORE POWERFUL REDUCTION IN SPASTICITY AND PAIN CAN BE ACHIEVED, WITH FEWER SIDE EFFECTS.4
Who Gablofen Helps
Gablofen, intrathecal baclofen, treats patients who have experienced a stroke, brain or spinal cord injury, or have been diagnosed with Multiple Sclerosis, or Cerebral Palsy and experience side effects such as muscle tightness, spasms, and fatigue, and frozen or stiff joints. Through use of Gablofen, spasticity is reduced, patients are more agile, and experience more independence.
If your patients are currently taking oral baclofen and not seeing relief of their spasticity or are having side effects from it, consider treating them with Gablofen, intrathecal baclofen.
5 Conditions that Lead to Severe Spasticity
The Gablofen Difference
When you choose Gablofen for your patients’ intrathecal baclofen therapy needs, you’re getting more than just a product for spasticity treatment and management. Gablofen is part of Piramal Critical Care, which means you get access to the entire care team and resources, leading to your partner in care. This includes Territory Managers and Customer Service Specialists who provide customized support, educational trainings and programs including roundtables, speaker events, and in-person trainings, and opportunities for you to provide feedback on how we can further assist you.
Piramal Critical Care is the market share leader in the U.S. for ITB use products and has been proven safe and effective through more than 10 years of intrathecal applications. We are ready to be your dedicated intrathecal team and are here to support you with collaboration, education, and convenient products.
Easy-to-Use Products
Safe for patients and medical providers
Conveniently packaged in prefilled syringes and vials
Streamlined drug administration
Precise amounts reduce risk of over- or under-filling the pump

Learn More
Eliminates the need to draw, measure, or dilute medication
No need to break glass ampules, reducing risk of sharps injury
Reduces risk of drug contamination
Manufactured with a high level of sterility
Customized Support
Support and assistance from Territory Managers and Customer Service Specialists
Ongoing educational opportunities for clinicians to support use accuracy, injection confidence, and comfort
Robust training and support network

Learn More
Speaker Programs
4 session, unbranded series
Efficient and Effective
on-label FDA-approved ITB studied and approved for use in
the Medtronic SynchroMed II Programmable Pump2
Only FDA-approved intrathecal baclofen packaged in vials and prefilled syringes

Learn More
Concentrated, targeted drug delivery provides:
Stronger reaction
Fewer side effects
Continued efficacy
Improved mobility
Gablofen Comes in the Following Options
Option 1: Prefilled Syringes
Prefilled syringes are available in one screening trial concentration and three refill concentrations, including2:

The 50mcg/mL screening dose allows your patients to receive an injection of Gablofen and experience the drug’s effects before undergoing pump implantation to start ITB therapy with Gablofen. Learn more about the screening dose and ITB therapy trial process.

Option 2: Factory-Sealed Vials
Factory-sealed vials are available in three refill concentrations, including2:
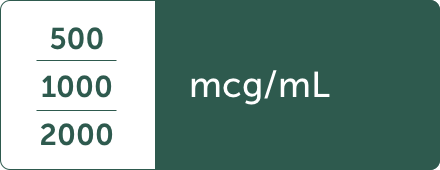
Gablofen Refill Kits
Orders of Gablofen will qualify for a complimentary Pump Refill Convenience Kit, shipped separately, which has everything you need to perform pump refills with Gablofen:
![]() Specifically designed for use with Gablofen
Specifically designed for use with Gablofen
![]() Each kit contains enough supplies for a 20 mL or 40 mL pump refill
Each kit contains enough supplies for a 20 mL or 40 mL pump refill
![]() Drug packaged separately from kit for more flexible storage
Drug packaged separately from kit for more flexible storage
![]() Latex-free kits are sterilized by ethylene oxide (ETO)
Latex-free kits are sterilized by ethylene oxide (ETO)
Understand Why Leading Physicians Utilize Gablofen

Dr. Chris Cronsell, MD, is the Director of Neurorehabilitation at the Center for Neurological Disorders Ascension Health Care. Cronsell specializes in spasticity management.

Dr. Moberg-Wolff, MD, is the Medical Director at Pediatric Rehabilitation Medicine Associates, LLC. She specializes in pediatric rehab medicine and brain injury medicine.
Have a Specific Question?
Important Risk Information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Gablofen® (baclofen injection) is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) ergic agonist indicated for use in the management of severe spasticity of cerebral or spinal origin in adult and pediatric patients age 4 years and above.
- Gablofen should be reserved for patients unresponsive to oral baclofen therapy, or those who experience intolerable central nervous system side effects at effective doses.
- Patients should first respond to a screening dose of intrathecal baclofen prior to consideration for long term infusion via an implantable pump.
- Spasticity due to traumatic brain injury: wait at least one year after injury before considering Gablofen therapy.
IMPORTANT RISK INFORMATION
WARNING: DO NOT DISCONTINUE ABRUPTLY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning
Abrupt discontinuation of intrathecal baclofen, regardless of the cause, has resulted in sequelae that include high fever, altered mental status, exaggerated rebound spasticity, and muscle rigidity, that in rare cases has advanced to rhabdomyolysis, multiple organ-system failure and death.
Prevention of abrupt discontinuation of intrathecal baclofen requires careful attention to programming and monitoring of the infusion system, refill scheduling and procedures, and pump alarms. Patients and caregivers should be advised of the importance of keeping scheduled refill visits and should be educated on the early symptoms of baclofen withdrawal. Special attention should be given to patients at apparent risk (e.g. spinal cord injuries at T-6 or above, communication difficulties, history of withdrawal symptoms from oral or intrathecal baclofen). Consult the technical manual of the implantable infusion system for additional post-implant clinician and patient information.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Hypersensitivity to baclofen.
- Do not use Gablofen for intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous or epidural administration.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Risk of life-threatening overdose during pump refills. Use extreme caution when filling the Medtronic SynchroMed® II Programmable Pump which is equipped with an injection port that allows direct access to the intrathecal catheter. Direct injection into the catheter through the catheter access port may cause a life-threatening overdose.
- Use only with Medtronic SynchroMed II Programmable Pump (or other pumps labeled for intrathecal administration of Gablofen (baclofen injection)).
- Potential for contamination due to non-sterile external surface of prefilled syringe. Although the drug solution and pathway in the Gablofen prefilled syringes are sterile, the external surface of the prefilled syringes (all strengths, including the 50 mcg/mL strength) are non-sterile and have the potential to lead to contamination and consequent adverse reactions. The use of Gablofen prefilled syringe in an aseptic setting (e.g., operating room) to fill sterile intrathecal pumps prior to implantation in patients is not recommended, unless the external surface of the prefilled syringe is treated to ensure sterility. Gablofen supplied in vials may be used with conventional aseptic technique to fill intrathecal pumps prior to implantation.
- Resuscitative equipment and trained staff must be available during screening dose, dose titration, and refills due to the potential life-threatening CNS depression, cardiovascular collapse, and/or respiratory failure.
- Overdose may cause drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, somnolence, respiratory depression, seizures, rostral progression of hypotonia and loss of consciousness progressing to coma.
- Use with caution in patients with psychotic disorders, schizophrenia or confusional states as it may exacerbate condition(s).
- Fatalities have been reported with intrathecal baclofen use.
- Caution should be used in patients with a history of autonomic dysreflexia.
- Presence of infection may increase the risk of surgical complication and complicate dosing of Gablofen.
- May cause drowsiness: use caution in operation of automobiles, dangerous machinery and activity that may be hazardous by decreased alertness. Other CNS depressants and alcohol may add to this effect.
- Potential development of intrathecal mass formation. Clinicians should monitor for signs and symptoms of new neurologic symptoms including the use of imaging diagnostic modalities.
- Oral baclofen use has been associated with a dose-related increase in incidence of ovarian cysts.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Serious Adverse Reactions
- Sudden withdrawal of Gablofen can result in serious complications that include high fever, confusion, muscle stiffness, multiple organ-system failure, and death. Inform patients that early symptoms of Gablofen withdrawal may include increased spasticity, itching, and tingling of extremities. If Gablofen withdrawal or a pump malfunction is suspected, patients should be brought immediately to a hospital for assessment and treatment.
- Gablofen overdose may occur suddenly or insidiously, and symptoms may include confusion, drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, slow or shallow breathing, seizures, loss of muscle tone, loss of consciousness, and coma.
- Other serious adverse events may include: potential development of intrathecal mass formation, drainage, infection, meningitis, unmanageable trunk control, CSF leakage, coma and death.
- Common Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions in patients with spasticity of spinal origin were hypotonia (25.3%), somnolence (20.9%), dizziness, nausea/vomiting, hypotension, headache, and convulsions.
- The most common adverse reactions in patients with spasticity of cerebral origin were hypotonia (34.7%), somnolence (18.7%), headache (10.7%), agitation, constipation, leukocytosis, chills, and urinary retention.
- Other common adverse events may include hypoventilation, hypertonia, paresthesia, increased salivation, back pain, pruritus, diarrhea, peripheral edema, asthenia, pain, confusion, speech disorder, amblyopia, accidental injury, and dry mouth.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy Category C. The effect of baclofen in labor and delivery is unknown.
- Breastfeeding: Baclofen is excreted into breast milk at oral therapeutic doses.
- Pediatric use: Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 4 years have not been established.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Gablofen® (baclofen injection) is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) ergic agonist indicated for use in the management of severe spasticity of cerebral or spinal origin in adult and pediatric patients age 4 years and above.
- Gablofen should be reserved for patients unresponsive to oral baclofen therapy, or those who experience intolerable central nervous system side effects at effective doses.
- Patients should first respond to a screening dose of intrathecal baclofen prior to consideration for long term infusion via an implantable pump.
- Spasticity due to traumatic brain injury: wait at least one year after injury before considering Gablofen therapy.
IMPORTANT RISK INFORMATION
WARNING: DO NOT DISCONTINUE ABRUPTLY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning
Abrupt discontinuation of intrathecal baclofen, regardless of the cause, has resulted in sequelae that include high fever, altered mental status, exaggerated rebound spasticity, and muscle rigidity, that in rare cases has advanced to rhabdomyolysis, multiple organ-system failure and death.
Prevention of abrupt discontinuation of intrathecal baclofen requires careful attention to programming and monitoring of the infusion system, refill scheduling and procedures, and pump alarms. Patients and caregivers should be advised of the importance of keeping scheduled refill visits and should be educated on the early symptoms of baclofen withdrawal. Special attention should be given to patients at apparent risk (e.g. spinal cord injuries at T-6 or above, communication difficulties, history of withdrawal symptoms from oral or intrathecal baclofen). Consult the technical manual of the implantable infusion system for additional post-implant clinician and patient information.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Hypersensitivity to baclofen.
- Do not use Gablofen for intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous or epidural administration.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Risk of life-threatening overdose during pump refills. Use extreme caution when filling the Medtronic SynchroMed® II Programmable Pump which is equipped with an injection port that allows direct access to the intrathecal catheter. Direct injection into the catheter through the catheter access port may cause a life-threatening overdose.
- Use only with Medtronic SynchroMed II Programmable Pump (or other pumps labeled for intrathecal administration of Gablofen (baclofen injection)).
- Potential for contamination due to non-sterile external surface of prefilled syringe. Although the drug solution and pathway in the Gablofen prefilled syringes are sterile, the external surface of the prefilled syringes (all strengths, including the 50 mcg/mL strength) are non-sterile and have the potential to lead to contamination and consequent adverse reactions. The use of Gablofen prefilled syringe in an aseptic setting (e.g., operating room) to fill sterile intrathecal pumps prior to implantation in patients is not recommended, unless the external surface of the prefilled syringe is treated to ensure sterility. Gablofen supplied in vials may be used with conventional aseptic technique to fill intrathecal pumps prior to implantation.
- Resuscitative equipment and trained staff must be available during screening dose, dose titration, and refills due to the potential life-threatening CNS depression, cardiovascular collapse, and/or respiratory failure.
- Overdose may cause drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, somnolence, respiratory depression, seizures, rostral progression of hypotonia and loss of consciousness progressing to coma.
- Use with caution in patients with psychotic disorders, schizophrenia or confusional states as it may exacerbate condition(s).
- Fatalities have been reported with intrathecal baclofen use.
- Caution should be used in patients with a history of autonomic dysreflexia.
- Presence of infection may increase the risk of surgical complication and complicate dosing of Gablofen.
- May cause drowsiness: use caution in operation of automobiles, dangerous machinery and activity that may be hazardous by decreased alertness. Other CNS depressants and alcohol may add to this effect.
- Potential development of intrathecal mass formation. Clinicians should monitor for signs and symptoms of new neurologic symptoms including the use of imaging diagnostic modalities.
- Oral baclofen use has been associated with a dose-related increase in incidence of ovarian cysts.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Serious Adverse Reactions
- Sudden withdrawal of Gablofen can result in serious complications that include high fever, confusion, muscle stiffness, multiple organ-system failure, and death. Inform patients that early symptoms of Gablofen withdrawal may include increased spasticity, itching, and tingling of extremities. If Gablofen withdrawal or a pump malfunction is suspected, patients should be brought immediately to a hospital for assessment and treatment.
- Gablofen overdose may occur suddenly or insidiously, and symptoms may include confusion, drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, slow or shallow breathing, seizures, loss of muscle tone, loss of consciousness, and coma.
- Other serious adverse events may include: potential development of intrathecal mass formation, drainage, infection, meningitis, unmanageable trunk control, CSF leakage, coma and death.
- Common Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions in patients with spasticity of spinal origin were hypotonia (25.3%), somnolence (20.9%), dizziness, nausea/vomiting, hypotension, headache, and convulsions.
- The most common adverse reactions in patients with spasticity of cerebral origin were hypotonia (34.7%), somnolence (18.7%), headache (10.7%), agitation, constipation, leukocytosis, chills, and urinary retention.
- Other common adverse events may include hypoventilation, hypertonia, paresthesia, increased salivation, back pain, pruritus, diarrhea, peripheral edema, asthenia, pain, confusion, speech disorder, amblyopia, accidental injury, and dry mouth.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy Category C. The effect of baclofen in labor and delivery is unknown.
- Breastfeeding: Baclofen is excreted into breast milk at oral therapeutic doses.
- Pediatric use: Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 4 years have not been established.
Important Risk Information
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Gablofen® (baclofen injection) is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) ergic agonist indicated for use in the management of severe spasticity of cerebral or spinal origin in adult and pediatric patients age 4 years and above.
- Gablofen should be reserved for patients unresponsive to oral baclofen therapy, or those who experience intolerable central nervous system side effects at effective doses.
- Patients should first respond to a screening dose of intrathecal baclofen prior to consideration for long term infusion via an implantable pump.
- Spasticity due to traumatic brain injury: wait at least one year after injury before considering Gablofen therapy.
IMPORTANT RISK INFORMATION
WARNING: DO NOT DISCONTINUE ABRUPTLY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning
Abrupt discontinuation of intrathecal baclofen, regardless of the cause, has resulted in sequelae that include high fever, altered mental status, exaggerated rebound spasticity, and muscle rigidity, that in rare cases has advanced to rhabdomyolysis, multiple organ-system failure and death.
Prevention of abrupt discontinuation of intrathecal baclofen requires careful attention to programming and monitoring of the infusion system, refill scheduling and procedures, and pump alarms. Patients and caregivers should be advised of the importance of keeping scheduled refill visits and should be educated on the early symptoms of baclofen withdrawal. Special attention should be given to patients at apparent risk (e.g. spinal cord injuries at T-6 or above, communication difficulties, history of withdrawal symptoms from oral or intrathecal baclofen). Consult the technical manual of the implantable infusion system for additional post-implant clinician and patient information.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to baclofen.
Do not use Gablofen for intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous or epidural administration.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Risk of life-threatening overdose during pump refills. Use extreme caution when filling the Medtronic SynchroMed® II Programmable Pump which is equipped with an injection port that allows direct access to the intrathecal catheter. Direct injection into the catheter through the catheter access port may cause a life-threatening overdose.
Use only with Medtronic SynchroMed® II Programmable Pump (or other pumps labeled for intrathecal administration of Gablofen (baclofen injection)).
Potential for contamination due to non-sterile external surface of prefilled syringe. Although the drug solution and pathway in the Gablofen prefilled syringes are sterile, the external surface of the prefilled syringes (all strengths, including the 50 mcg/mL strength) are non-sterile and have the potential to lead to contamination and consequent adverse reactions. The use of Gablofen prefilled syringe in an aseptic setting (e.g., operating room) to fill sterile intrathecal pumps prior to implantation in patients is not recommended, unless the external surface of the prefilled syringe is treated to ensure sterility. Gablofen supplied in vials may be used with conventional aseptic technique to fill intrathecal pumps prior to implantation.
Resuscitative equipment and trained staff must be available during screening dose, dose titration, and refills due to the potential life-threatening CNS depression, cardiovascular collapse, and/or respiratory failure.
Overdose may cause drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, somnolence, respiratory depression, seizures, rostral progression of hypotonia and loss of consciousness progressing to coma.
Use with caution in patients with psychotic disorders, schizophrenia or confusional states as it may exacerbate condition(s).
Fatalities have been reported with intrathecal baclofen use.
Caution should be used in patients with a history of autonomic dysreflexia.
Presence of infection may increase the risk of surgical complication and complicate dosing of Gablofen.
May cause drowsiness: use caution in operation of automobiles, dangerous machinery and activity that may be hazardous by decreased alertness. Other CNS depressants and alcohol may add to this effect.
Potential development of intrathecal mass formation. Clinicians should monitor for signs and symptoms of new neurologic symptoms including the use of imaging diagnostic modalities.
Oral baclofen use has been associated with a dose-related increase in incidence of ovarian cysts.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Serious Adverse Reactions
- Sudden withdrawal of Gablofen can result in serious complications that include high fever, confusion, muscle stiffness, multiple organ-system failure, and death. Inform patients that early symptoms of Gablofen withdrawal may include increased spasticity, itching, and tingling of extremities. If Gablofen withdrawal or a pump malfunction is suspected, patients should be brought immediately to a hospital for assessment and treatment.
- Gablofen overdose may occur suddenly or insidiously, and symptoms may include confusion, drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, slow or shallow breathing, seizures, loss of muscle tone, loss of consciousness, and coma.
- Other serious adverse events may include: potential development of intrathecal mass formation, drainage, infection, meningitis, unmanageable trunk control, CSF leakage, coma and death.
Common Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions in patients with spasticity of spinal origin were hypotonia (25.3%), somnolence (20.9%), dizziness, nausea/vomiting, hypotension, headache, and convulsions.
- The most common adverse reactions in patients with spasticity of cerebral origin were hypotonia (34.7%), somnolence (18.7%), headache (10.7%), agitation, constipation, leukocytosis, chills, and urinary retention.
- Other common adverse events may include hypoventilation, hypertonia, paresthesia, increased salivation, back pain, pruritus, diarrhea, peripheral edema, asthenia, pain, confusion, speech disorder, amblyopia, accidental injury, and dry mouth.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy Category C. The effect of baclofen in labor and delivery is unknown.
Breastfeeding: Baclofen is excreted into breast milk at oral therapeutic doses.
Pediatric use: Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 4 years have not been established.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Gablofen® (baclofen injection) is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) ergic agonist indicated for use in the management of severe spasticity of cerebral or spinal origin in adult and pediatric patients age 4 years and above.
- Gablofen should be reserved for patients unresponsive to oral baclofen therapy, or those who experience intolerable central nervous system side effects at effective doses.
- Patients should first respond to a screening dose of intrathecal baclofen prior to consideration for long term infusion via an implantable pump.
- Spasticity due to traumatic brain injury: wait at least one year after injury before considering Gablofen therapy.
IMPORTANT RISK INFORMATION
WARNING: DO NOT DISCONTINUE ABRUPTLY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning
Abrupt discontinuation of intrathecal baclofen, regardless of the cause, has resulted in sequelae that include high fever, altered mental status, exaggerated rebound spasticity, and muscle rigidity, that in rare cases has advanced to rhabdomyolysis, multiple organ-system failure and death.
Prevention of abrupt discontinuation of intrathecal baclofen requires careful attention to programming and monitoring of the infusion system, refill scheduling and procedures, and pump alarms. Patients and caregivers should be advised of the importance of keeping scheduled refill visits and should be educated on the early symptoms of baclofen withdrawal. Special attention should be given to patients at apparent risk (e.g. spinal cord injuries at T-6 or above, communication difficulties, history of withdrawal symptoms from oral or intrathecal baclofen). Consult the technical manual of the implantable infusion system for additional post-implant clinician and patient information.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to baclofen.
Do not use Gablofen for intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous or epidural administration.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Risk of life-threatening overdose during pump refills. Use extreme caution when filling the Medtronic SynchroMed® II Programmable Pump which is equipped with an injection port that allows direct access to the intrathecal catheter. Direct injection into the catheter through the catheter access port may cause a life-threatening overdose.
Use only with Medtronic SynchroMed® II Programmable Pump (or other pumps labeled for intrathecal administration of Gablofen (baclofen injection)).
Potential for contamination due to non-sterile external surface of prefilled syringe. Although the drug solution and pathway in the Gablofen prefilled syringes are sterile, the external surface of the prefilled syringes (all strengths, including the 50 mcg/mL strength) are non-sterile and have the potential to lead to contamination and consequent adverse reactions. The use of Gablofen prefilled syringe in an aseptic setting (e.g., operating room) to fill sterile intrathecal pumps prior to implantation in patients is not recommended, unless the external surface of the prefilled syringe is treated to ensure sterility. Gablofen supplied in vials may be used with conventional aseptic technique to fill intrathecal pumps prior to implantation.
Resuscitative equipment and trained staff must be available during screening dose, dose titration, and refills due to the potential life-threatening CNS depression, cardiovascular collapse, and/or respiratory failure.
Overdose may cause drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, somnolence, respiratory depression, seizures, rostral progression of hypotonia and loss of consciousness progressing to coma.
Use with caution in patients with psychotic disorders, schizophrenia or confusional states as it may exacerbate condition(s).
Fatalities have been reported with intrathecal baclofen use.
Caution should be used in patients with a history of autonomic dysreflexia.
Presence of infection may increase the risk of surgical complication and complicate dosing of Gablofen.
May cause drowsiness: use caution in operation of automobiles, dangerous machinery and activity that may be hazardous by decreased alertness. Other CNS depressants and alcohol may add to this effect.
Potential development of intrathecal mass formation. Clinicians should monitor for signs and symptoms of new neurologic symptoms including the use of imaging diagnostic modalities.
Oral baclofen use has been associated with a dose-related increase in incidence of ovarian cysts.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Serious Adverse Reactions
- Sudden withdrawal of Gablofen can result in serious complications that include high fever, confusion, muscle stiffness, multiple organ-system failure, and death. Inform patients that early symptoms of Gablofen withdrawal may include increased spasticity, itching, and tingling of extremities. If Gablofen withdrawal or a pump malfunction is suspected, patients should be brought immediately to a hospital for assessment and treatment.
- Gablofen overdose may occur suddenly or insidiously, and symptoms may include confusion, drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, slow or shallow breathing, seizures, loss of muscle tone, loss of consciousness, and coma.
- Other serious adverse events may include: potential development of intrathecal mass formation, drainage, infection, meningitis, unmanageable trunk control, CSF leakage, coma and death.
Common Adverse Reactions
- The most common adverse reactions in patients with spasticity of spinal origin were hypotonia (25.3%), somnolence (20.9%), dizziness, nausea/vomiting, hypotension, headache, and convulsions.
- The most common adverse reactions in patients with spasticity of cerebral origin were hypotonia (34.7%), somnolence (18.7%), headache (10.7%), agitation, constipation, leukocytosis, chills, and urinary retention.
- Other common adverse events may include hypoventilation, hypertonia, paresthesia, increased salivation, back pain, pruritus, diarrhea, peripheral edema, asthenia, pain, confusion, speech disorder, amblyopia, accidental injury, and dry mouth.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy Category C. The effect of baclofen in labor and delivery is unknown.
Breastfeeding: Baclofen is excreted into breast milk at oral therapeutic doses.
Pediatric use: Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 4 years have not been established.